What Is A GPU And How To Choose The Ideal Graphics Card
Master GPU selection with expert tips for gaming, AI, content creation. Compare types, specs & find your ideal graphics card today.
Ever wonder why your friend's computer runs games butter-smooth while yours stutters? The secret weapon is called a GPU, and understanding it might be the game-changer you've been looking for.
Whether you're building your first gaming setup, starting content creation, or diving into AI, choosing the right GPU can feel overwhelming. But here's the good news: it doesn't have to be complicated.
In this guide, you'll discover exactly what makes GPUs tick, how they differ from regular processors, and most importantly, how to pick one that matches your needs and budget perfectly. No confusing jargon, just practical advice you can use today.
Summary
- What Makes GPUs Special And How They Work
- GPU Versus CPU: Why Both Matter For Your Computer
- Different GPU Types: Finding Your Perfect Match
- Beyond Gaming: Surprising Ways GPUs Power Modern Tech
- Choosing Your Ideal Graphics Card Made Simple
- Understanding Performance: Benchmarks Explained Clearly
- Cloud GPUs: Powerful Graphics Without Buying Hardware
- Frequently Asked Questions
What Makes GPUs Special And How They Work
A Graphics Processing Unit is basically a super-powered calculator designed specifically for handling images, videos, and animations. Think of it as having thousands of tiny workers all doing similar math problems at the same time.
Unlike your computer's main brain (the CPU) that tackles tasks one by one, GPUs contain hundreds or thousands of smaller cores working together. This parallel processing makes them incredibly fast for specific jobs.
Here's what makes GPUs so powerful:
Parallel Processing Magic: While CPUs have 4-16 powerful cores for complex tasks, modern GPUs pack thousands of simpler cores. This design is perfect for breaking down big jobs into many small, similar calculations.
Dedicated Fast Memory: GPUs come with their own specialized memory called VRAM, usually GDDR6 or GDDR6X technology. This memory handles huge amounts of visual data lightning-fast.
Purpose-Built Design: Everything inside a GPU is optimized for the mathematical operations needed in graphics, like matrix multiplication and floating-point calculations.
The evolution has been remarkable. Back in the 1990s, everything ran through the CPU, making 3D graphics painfully slow. NVIDIA's GeForce 256 in 1999 changed everything by moving graphics to a dedicated chip.
Today's GPUs handle way more than just graphics. They power machine learning, cryptocurrency mining, and scientific simulations. This versatility makes them essential in modern computing.
The technology keeps advancing rapidly. Modern GPUs don't just push pixels anymore. They accelerate AI training, help scientists model climate change, and even assist doctors in medical imaging analysis.
GPU Versus CPU: Why Both Matter For Your Computer
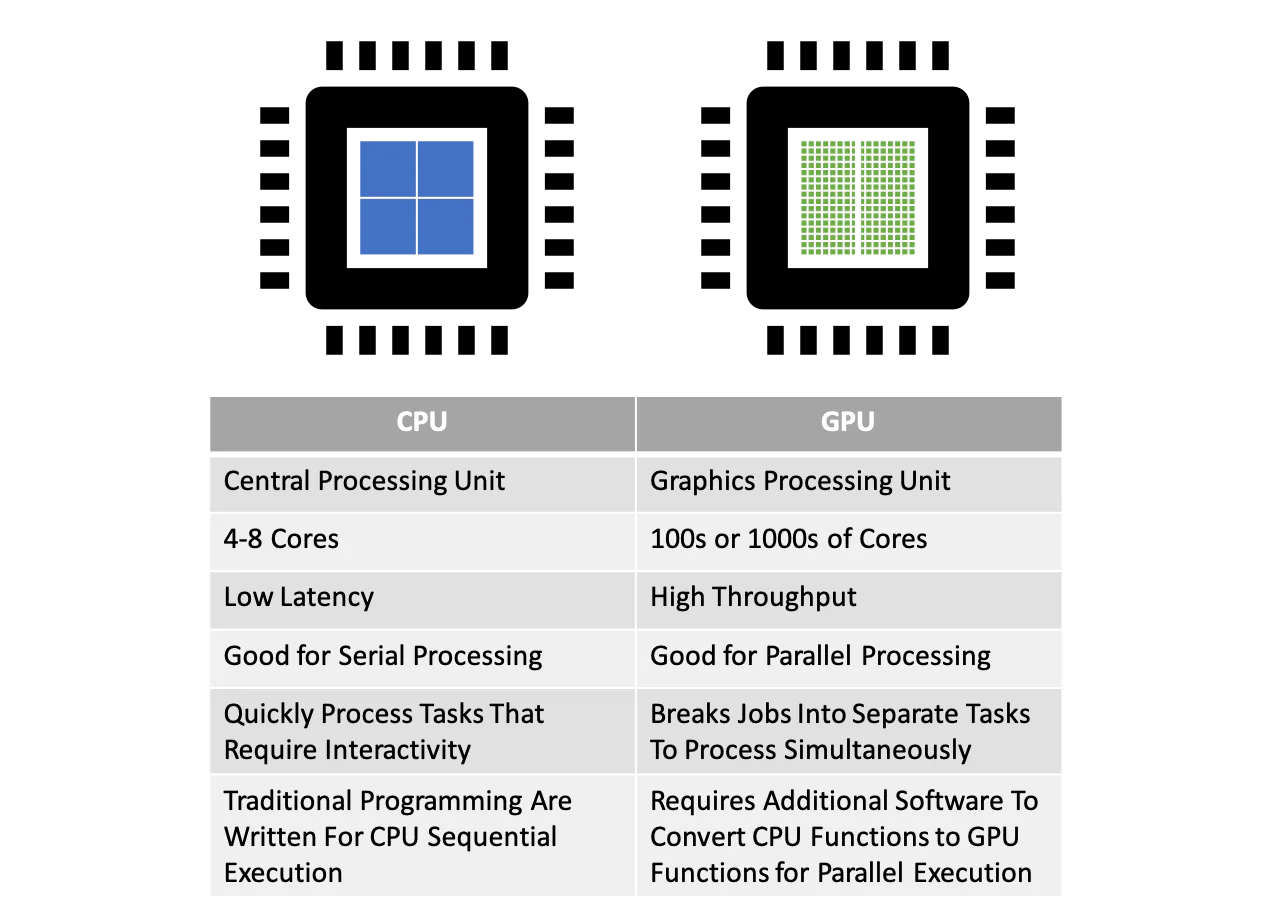
Understanding the CPU-GPU partnership helps you make smarter hardware choices. Both are processors, but they're designed for completely different jobs.
What CPUs Do Best:
CPUs handle general-purpose computing. They excel at complex decision-making tasks, running your operating system, managing files, and coordinating all your applications. Think of them as the orchestra conductor keeping everything in sync.
What GPUs Excel At:
GPUs specialize in parallel computing. They're built for handling thousands of simple calculations simultaneously, making them perfect for graphics rendering, AI training, video encoding, and scientific simulations.
Here's a practical comparison: imagine you need to solve 1,000 simple math problems. A CPU would solve them one by one super quickly. A GPU would tackle many at once, potentially finishing the entire batch faster.
This fundamental difference explains their strengths:
CPU Strengths:
- Complex logic and decision-making
- System management tasks
- Single-threaded applications
- Tasks requiring frequent branching
GPU Strengths:
- Graphics rendering and image processing
- Machine learning and AI workloads
- Video encoding and decoding
- Scientific simulations

For most tasks today, you need both working together harmoniously. The CPU manages your system and makes complex decisions, while the GPU accelerates compute-intensive workloads. This partnership delivers the best overall performance.
Modern computing relies on this balance. When you're gaming, the CPU handles game logic and AI while the GPU renders beautiful visuals. When editing videos, the CPU manages your project timeline while the GPU processes effects and exports footage.
Different GPU Types: Finding Your Perfect Match
Not all GPUs are created equal. Understanding the three main types helps you choose the right solution for your specific needs and budget.
Discrete GPUs: Maximum Power
Discrete GPUs are standalone graphics processors on their own circuit board, separate from your CPU. These are what most people picture when they hear "graphics card."
Key Features:
These come as separate chips with dedicated cooling systems. They have their own power connections (usually 6-pin, 8-pin, or newer 12-pin connectors). They include dedicated VRAM ranging from 8GB to 24GB or more.
Best For:
Gaming enthusiasts wanting high frame rates and stunning visuals love these. Content creators working with 4K video or complex 3D rendering rely on them. AI researchers and machine learning practitioners need their power.
Popular Options:
NVIDIA GeForce RTX series leads the pack with options like RTX 4060, RTX 4070, and RTX 4080. AMD Radeon RX series offers strong competition with RX 7600 and RX 7900 XTX. Intel Arc series provides newer alternatives with Arc A750 and Arc A770.
Integrated GPUs: Efficient And Affordable
Integrated GPUs live directly inside your CPU chip, sharing system memory and power. They've become surprisingly capable recently.
Key Features:
Built into the CPU means no separate card needed. They share system RAM instead of having dedicated VRAM. Lower power consumption makes them ideal for laptops. No additional cost beyond the CPU itself.
Best For:
Everyday computing like web browsing, office work, and media streaming works great. Light gaming at 1080p with modest settings is possible. Laptops prioritizing battery life and thin design benefit most.
Notable Examples:
Intel Iris Xe Graphics in 11th gen and newer Intel CPUs performs well. AMD Radeon Graphics in Ryzen APUs offers competitive performance. Apple M-series integrated graphics in MacBooks delivers impressive results.
Virtual GPUs: Cloud-Based Power
Virtual GPUs provide GPU capabilities through cloud services without owning physical hardware. They're accessed through internet-connected data centers.
Key Features:
No physical hardware to maintain or worry about. Scalable resources adjust based on current needs. Pay-as-you-use pricing models keep costs flexible. Access high-end GPU power without massive upfront investment.
Best For:
Startups and small businesses needing occasional high-performance computing benefit greatly. Students learning AI without expensive hardware find them perfect. Remote workers needing GPU acceleration temporarily appreciate the flexibility.
If you're setting up a complete workstation, consider pairing your GPU choice with ergonomic accessories for maximum comfort during long sessions.
Beyond Gaming: Surprising Ways GPUs Power Modern Tech
While gaming put GPUs on the map, today's graphics processors drive an incredible range of applications far beyond entertainment. Let's explore how GPUs are changing various industries.
Gaming And Entertainment Evolution
Gaming remains GPU's most visible application, but modern demands are more intensive than ever.
4K Gaming renders games at 3840×2160 resolution, requiring roughly 4 times more processing power than standard 1080p gaming. High Refresh Rate Gaming targets 144Hz, 240Hz, or even 360Hz displays, demanding GPUs render frames much faster than traditional 60fps.
Ray Tracing simulates realistic lighting, reflections, and shadows in real-time using dedicated cores. Virtual Reality demands consistent high frame rates (90-120fps minimum) at high resolutions to prevent motion sickness.
Content Creation Revolution
Video Editing gets massive acceleration. GPUs handle video encoding, effects processing, and real-time preview generation. A powerful GPU can reduce 4K video export times from hours to minutes.
3D Rendering speeds up dramatically. Professional artists using Blender, Maya, and Cinema 4D see GPU rendering that's 10-50 times faster than CPU-only rendering for certain workloads.
Live Streaming benefits hugely. GPUs handle real-time video encoding for Twitch and YouTube, allowing streamers to broadcast high-quality content without impacting game performance.

Artificial Intelligence Breakthrough
This represents perhaps the most exciting growth area for GPU applications.
AI Model Training requires massive parallel processing power. GPUs reduce training time from weeks to days or even hours for large neural networks. Inference And Deployment of trained AI models for real-time predictions benefits enormously from GPU acceleration.
Computer Vision applications like image recognition, object detection, and medical imaging analysis leverage GPU power. Natural Language Processing for large language models and chatbots relies heavily on GPU processing.
Scientific Computing Advances
Climate Modeling for weather prediction and climate research processes vast amounts of data through complex mathematical models.
Medical Research including drug discovery, protein folding simulation, and medical imaging analysis all benefit from GPU acceleration. Astronomy And Physics simulations of galaxy formation and particle interactions require massive computational power.
Choosing Your Ideal Graphics Card Made Simple
Finding the right GPU involves balancing performance needs, budget limits, and future-proofing. Here's a systematic approach to making the perfect choice for you.
Define Your Primary Purpose
Budget Gaming (1080p):
Target 60fps at 1920×1080 resolution with medium-high settings. Consider RTX 4060, RX 7600, or Intel Arc A750. Budget between $200-300 and look for minimum 8GB VRAM.
Enthusiast Gaming (1440p or 4K):
Target 60-120fps at 2560×1440 or 3840×2160 with high settings. Look at RTX 4070 Super, RTX 4080, or RX 7800 XT. Budget $500-800 and aim for 12GB or more VRAM.
Content Creation:
Video editing benefits from CUDA cores (NVIDIA) or Stream Processors (AMD). 3D rendering performance depends on your specific render engine. Consider RTX 4070 or higher for serious professional work. Look for 16GB+ VRAM for 4K video editing.
AI And Machine Learning:
Training workloads generally prefer NVIDIA GPUs due to CUDA ecosystem maturity. Inference tasks work well on both NVIDIA and AMD options. Consider RTX 4080 or higher for serious AI work with 16GB+ VRAM essential.

Key Technical Specifications
Video Memory (VRAM):
8GB suffices for 1080p gaming and light content creation. 12-16GB proves ideal for 1440p gaming and professional work. 20GB+ provides future-proofing for 4K gaming and heavy AI workloads.
Memory Type And Bandwidth:
GDDR6 remains standard for most modern GPUs. GDDR6X offers higher bandwidth in premium GPUs. Wider memory bus widths (256-bit, 384-bit) generally mean better performance.
Cooling And Power:
Check your power supply capacity since GPUs can require 200-450W. Ensure adequate case ventilation for proper airflow. Consider custom cooling solutions for high-end cards if needed.
Budget-Based Recommendations
Entry Level ($200-400):
RTX 4060 8GB delivers excellent 1080p gaming performance. RX 7600 8GB provides strong AMD alternative with good value. RTX 4060 Ti 16GB offers more VRAM for content creation needs.
Mid-Range ($400-700):
RTX 4070 Super 12GB provides great 1440p performance with ray tracing. RX 7700 XT 12GB offers competitive rasterization performance. RTX 4070 Ti Super 16GB handles high-end 1440p and entry-level 4K.
High-End ($700-1200):
RTX 4080 Super 16GB excels at 4K gaming and content creation. RX 7900 XTX 24GB delivers strong 4K performance with abundant VRAM.
Enthusiast ($1200+):
RTX 4090 24GB provides uncompromised 4K gaming and professional work capability. Professional cards like RTX A4000 and A5000 serve certified professional applications.
Future-Proofing Tips
Ray Tracing Support proves essential for modern gaming experiences moving forward. DLSS/FSR Support through AI upscaling technologies extends GPU lifespan significantly. AV1 Encoding matters for content creators and streamers. PCIe 4.0 Support ensures compatibility with modern motherboards.
Pair your GPU choice with a properly matched gaming monitor to maximize your investment and achieve your performance targets.
Understanding Performance: Benchmarks Explained Clearly
GPU benchmarks help you compare performance across different models and use cases. These standardized tests provide objective data for informed purchasing decisions.
Benchmark Types You'll Encounter
Synthetic Benchmarks:
These measure raw GPU performance under controlled conditions. 3DMark serves as industry-standard with various tests like Time Spy and Port Royal for ray tracing. Unigine Heaven and Superposition stress test GPUs to their limits.
Real-World Benchmarks:
These measure performance in actual games and applications. Game benchmarks test FPS in popular titles like Cyberpunk 2077 and Call of Duty. Professional application tests measure rendering times in Blender and video export speeds in Premiere Pro.
Key Performance Numbers
Frame Rate (FPS):
30-60 FPS provides playable experience but may feel choppy in fast-paced games. 60-120 FPS delivers smooth gaming experience. 120+ FPS proves ideal for competitive gaming and high refresh rate monitors.
Resolution Performance:
1080p serves as entry-level target where most GPUs achieve high settings comfortably. 1440p represents the sweet spot for modern gaming requiring mid to high-end GPU. 4K demands high-end GPUs for smooth performance.
Memory Bandwidth:
Measured in GB/s, this indicates how quickly the GPU accesses its memory. Higher bandwidth generally correlates with better performance at high resolutions and complex workloads.
Interpreting Results Correctly
Look For Consistency: A GPU performing well across multiple games and applications generally proves more reliable than one with inconsistent results.
Match Your Resolution: A GPU excelling at 1080p may struggle at 4K. Always match benchmark resolution to your intended use case.
Consider Features: Raw performance numbers don't tell the complete story. Features like ray tracing, DLSS, or specialized compute capabilities may justify performance trade-offs.
Check Multiple Sources: Different reviewers may get slightly different results. Look for consistent trends across multiple professional reviews.
Thermal And Power Factors
Thermal Management:
Most GPUs target 75-85°C under load as normal operating temperature. Consistent thermal throttling indicates inadequate cooling. Consider your case airflow when choosing GPU cooling solutions.
Power Consumption:
Entry-level GPUs consume 100-150W typically. Mid-range GPUs use 200-250W on average. High-end GPUs require 300-450W. Always ensure your power supply handles GPU plus system overhead.
Cloud GPUs: Powerful Graphics Without Buying Hardware
Cloud-based GPU services revolutionize access to high-performance computing. They make powerful GPUs available without expensive hardware purchases.
Understanding Cloud GPU Benefits
Cloud GPUs provide on-demand access to powerful graphics processing through internet-connected data centers. Instead of buying expensive hardware, you rent equivalent or superior capabilities.
Major Advantages:
No upfront investment required for accessing high-end hardware. Scalability lets you adjust resources up or down based on needs. Maintenance-free operation eliminates hardware concerns. Access to latest hardware becomes immediate without purchasing.
Potential Drawbacks:
Ongoing costs can become expensive for continuous heavy use. Internet dependency requires stable, high-bandwidth connection. Latency concerns make them unsuitable for real-time gaming. Data transfer costs add up when moving large datasets.
Popular Cloud Services
Google Cloud Platform:
Offers NVIDIA T4, V100, A100, and L4 GPUs with pay-per-hour pricing. Sustained use discounts reduce costs for longer sessions. Preemptible instances provide cost-effective batch processing.
Amazon Web Services:
Wide variety of GPU instances across P3, P4, G4, and G5 series. Spot instances deliver significant cost savings on flexible workloads. Strong integration with complete AWS ecosystem.
Microsoft Azure:
N-series virtual machines offer various GPU options. Azure Machine Learning service includes built-in GPU support. Strong integration with Microsoft development tools.
Specialized AI Platforms:
Google Colab provides free tier with limited GPU access and paid Pro versions. Paperspace Gradient focuses specifically on machine learning workflows. RunPod offers competitive pricing for AI development.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
When Cloud Makes Sense:
Learning AI without hardware investment proves cost-effective. Occasional 3D rendering or video processing projects benefit. Startups needing flexible compute resources save money. Research projects with variable computational demands work well.
When Local GPUs Win:
Daily gaming or content creation justifies ownership. Consistent, long-term GPU-intensive work pays back investment. Applications requiring low latency need local hardware. Privacy concerns with sensitive data favor local solutions.
Practical Usage Tips
Optimize Costs:
Use spot or preemptible instances when possible for 60-90% savings. Monitor usage carefully to avoid unexpected bills. Choose minimum GPU specification meeting your needs. Shut down instances when not actively using them.
Data Management:
Keep frequently accessed data in cloud storage attached to GPU instances. Use data transfer optimization techniques. Consider bandwidth costs when moving large datasets back and forth.
Performance Optimization:
Choose data center regions close to your location for better latency. Use appropriate instance types for your specific workload. Monitor resource utilization ensuring you're not overpaying for unused capacity.
For professionals balancing cloud and local solutions, quality home office setup enhances productivity regardless of computing power source.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much VRAM do I need for gaming and content creation?
For 1080p gaming, 8GB is sufficient. For 1440p gaming and video editing, aim for 12GB. For 4K gaming, AI work, or professional content creation, choose 16GB or more for future-proofing and handling demanding workloads.
Modern games increasingly demand more VRAM. Games like Cyberpunk 2077 with ray tracing can use over 10GB at 4K resolution. For future-proofing, err on the side of more VRAM.
Should I buy an older high-end GPU or a newer mid-range one?
Newer mid-range GPUs are typically better choices. They offer superior power efficiency, modern features like updated ray tracing, longer driver support, and often similar performance per dollar compared to older high-end models.
However, significant discounts on last-generation hardware might be worth considering if savings are substantial.
Can integrated graphics handle modern gaming?
Modern integrated graphics like Intel Iris Xe and AMD Radeon Graphics can handle many games at 1080p with low-medium settings. However, for smooth high-settings gaming or demanding titles, a discrete GPU is strongly recommended.
Apple M-series chips offer excellent performance for integrated graphics, sometimes matching entry-level discrete GPUs.
What's the difference between a GPU and a graphics card?
The GPU is the actual processing chip that handles computations. A graphics card is the complete circuit board that includes the GPU, memory chips, cooling system, and power connections. Think of it as engine versus complete car.
When people say "graphics card," they're usually referring to the entire package you install in your computer.
How often should I upgrade my GPU?
Casual gamers can upgrade every 4-6 years when performance becomes noticeably inadequate. Enthusiasts typically upgrade every 2-3 years to maintain high settings. Content creators should upgrade when render times hurt productivity. AI practitioners upgrade when VRAM limits their model capabilities.
Your specific needs and satisfaction level should guide upgrade timing rather than arbitrary schedules.
Does GPU brand matter for specific software?
Yes, software optimization varies significantly. NVIDIA offers superior performance in Adobe Creative Suite, most AI frameworks, and ray tracing applications. AMD provides often better value for pure rasterization gaming with good open-source support. Intel Arc continues establishing ecosystem support with rapid improvements.
Research your specific software's optimization before choosing.
Can I use multiple GPUs together?
Multi-GPU gaming setups are nearly obsolete now. SLI and CrossFire have minimal game support. However, multiple GPUs still benefit AI and compute workloads. You can also use different GPUs for separate purposes.
For gaming, investing in one powerful GPU beats multiple weaker ones.
How important is ray tracing for gaming?
Ray tracing grows increasingly important as more AAA games include these features. Visual quality improvements are significant in supported games. Performance impact decreases with better hardware and optimization. AI upscaling technologies like DLSS help offset performance costs.
If buying a GPU for 3-4 years, ray tracing capability is recommended for future compatibility.
Conclusion
Choosing the right GPU doesn't have to feel overwhelming. Whether you're building your first gaming PC, upgrading for content creation, or exploring AI development, matching your GPU to your specific needs and budget is what matters most.
Remember that the "best" GPU is simply the one delivering the performance you need at a price you're comfortable with. A mid-range GPU meeting your requirements beats an expensive high-end card exceeding them.
Take time researching benchmarks for your specific use cases. Consider reasonable future-proofing without overspending. Don't forget supporting components like adequate power supply and proper cooling.






